A motorcycle engine operates on the internal combustion principle, converting fuel into motion. It typically uses a four-stroke cycle to power the bike’s wheels.
Motorcycles captivate riders with their speed and agility, much of which owes to the engineering marvel of the motorcycle engine. At the heart of this powertrain is the four-stroke cycle: intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust.
These stages work in harmony to efficiently transform gasoline into the kinetic energy that propels the bike forward.
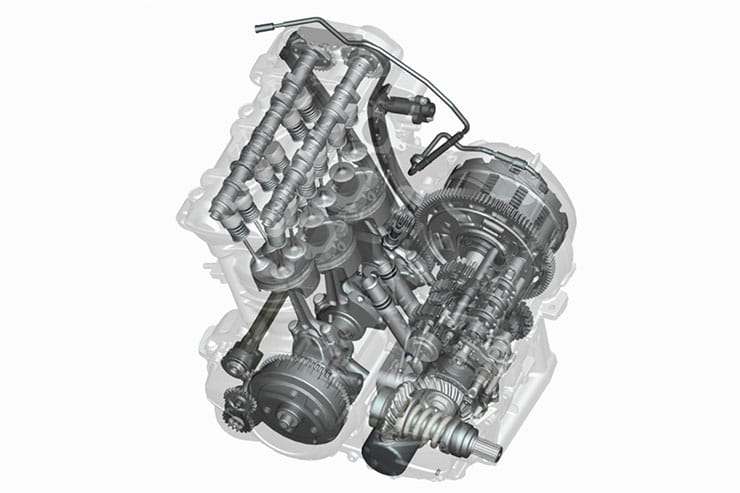
Motorcycle engines vary in size and design, from single-cylinder engines suitable for modest urban bikes, to roaring V-twins and multi-cylinder powerhouses for high-performance machines.
This technical symphony is orchestrated through a meticulous arrangement of cylinders, pistons, a fuel injection system, and an exhaust system, all designed for maximum efficiency.
Do you know how a motorcycle engine works? Enthusiasts and casual riders alike benefit from having these engineering fundamentals, enriching the riding experience and empowering them with knowledge for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Table of Contents
The Heart Of Ride: Motorcycle Engines
Welcome to the exhilarating world of two-wheeled machines and the epicenter of their power: the motorcycle engine. This marvel of engineering not only propels enthusiasts down the road but also captures hearts with its rhythmical roar.
Internal Combustion Basics
At the core of motorcycle engines lies the internal combustion process. Here’s how it works:
- Air and fuel mix within the engine’s chambers.
- The mixture is compressed by pistons.
- A spark ignites the mixture, causing explosions.
- These explosions drive pistons back and forth.
- The piston’s movement turns the crankshaft, creating power.
- Exhaust gases are ejected, clearing the way for a new cycle.

Credit: www.bennetts.co.uk
Engine Configuration And Types
Different bikes have different engine types and configurations. Here’s a snapshot:
| Engine Type | Features |
|---|---|
| Single Cylinder | Simple, for beginner bikes and off-roaders. |
| Parallel Twin | Two cylinders side by side, smooth and compact. |
| V-Twin | V-shaped, classic thump for cruisers. |
| Inline-Four | A quartet of cylinders, balanced high-performance. |
| Boxer | Opposed cylinders, unique for a lower center of gravity. |
Each type offers a unique riding experience, from the ruggedness of the single-cylinder to the refined power of the inline-four.
Fuel System: The Power Provider
The fuel system feeds your motorcycle’s engine the right mix of air and fuel. Think of it as the motorcycle’s stomach, processing energy for movement. A well-functioning fuel system ensures top performance, power, and efficiency.
Carburetion Vs. Fuel Injection
There are two main types of fuel systems: carburetion and fuel injection. Carburetors mix fuel with air using a simple, mechanical process. Fuel injection, on the other hand, uses electronics to spray fuel into the engine.
- Carburetors are often found on classic bikes.
- Fuel injectors are in modern motorcycles.
Air-fuel Mixing
The air-fuel mix is crucial for engine power. This mix sparks inside the engine to make it run. A perfect mix gives your bike the best power. Carburetors use jets to blend air and fuel. Fuel injectors atomize fuel for a finer mix.
| System | Air-Fuel Mix Method |
|---|---|
| Carburetor | Uses jets for mixing |
| Fuel Injection | Atomizes fuel for mixing |
Igniting The Charge: The Spark Of Life
Think of a motorcycle engine as a big pump. It mixes air and fuel and turns the mixture into power. This happens in a special part of the engine called the cylinder. But to make everything work, the engine needs a spark. This tiny bolt of electricity sets everything in motion. Let’s see how the spark plugs and electrical system make this happen.
Spark Plugs And Ignition Timing
In the heart of your motorcycle’s engine, spark plugs are the unsung heroes. They create a spark that ignites the air-fuel mix. The right spark at the right time makes the engine run well. Here are key things spark plugs do:
- Handle high temperature and pressure inside the cylinder
- Turn electrical energy into a spark
- Ignite the mix to push the piston down
Ignition timing is when the spark happens. It has to be perfect. If the timing is off, the engine won’t run right. Here’s what good timing helps with:
- Maximum power
- Better fuel economy
- Lower emissions
Electrical System’s Role
The electrical system is like a engine’s nervous system. It tells the spark plug when to fire. Here are the parts that work together:
- Battery: Stores the power
- Alternator: Makes electricity when the engine runs
- Ignition coil: Boosts the power from the battery
- Igniter: Controls the timing
Every part has to work perfectly to make a clean, strong spark. If even one part fails, the engine might not start. Or, it could run badly. Remember:
- Keep your battery charged
- Check the wiring for damage
- Replace old spark plugs
A healthy electrical system means a lively motorcycle. So give it the attention it deserves!

Credit: m.youtube.com
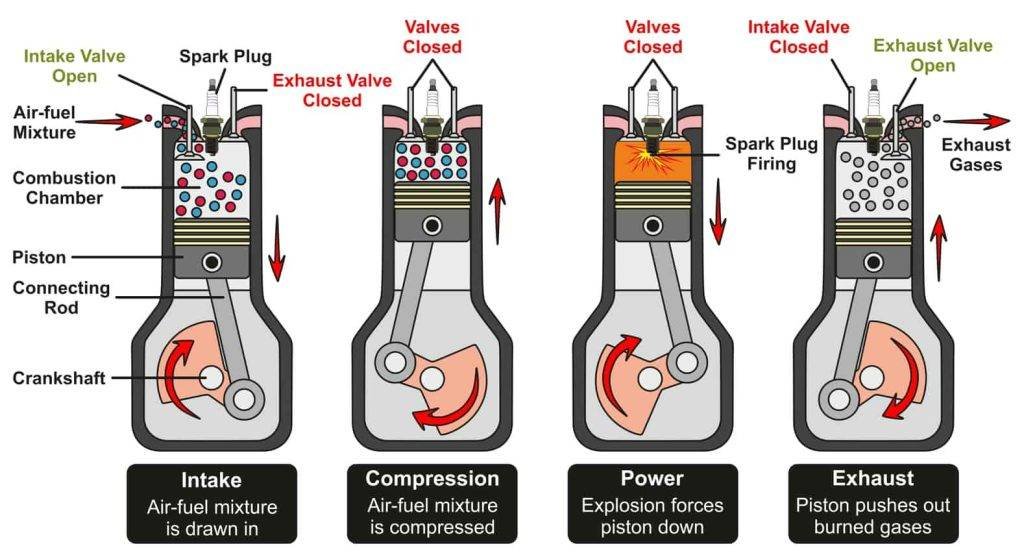
From Liquid To Motion: The Combustion Cycle
Imagine fuel turning into a powerful force that drives you forward. This magic happens inside a motorcycle engine through the combustion cycle. It’s a process that transforms liquid fuel into motion. Let’s break down this fascinating journey from fuel to fast lane.
Intake Stroke
Fresh air and fuel start their engine journey during the intake stroke. A valve opens. Air and fuel mix together into the engine cylinder. This mix waits for its turn to become energy.
Compression Stroke
The compression stroke is next. A piston inside the cylinder moves up. It squeezes the air-fuel mixture tightly. This makes the magic mix ready to explode with power.
Power Stroke
Then comes the power stroke. A spark plug gives life. It fires up the mix. Boom! The piston pushes down hard. This force turns the engine’s wheels. We’re now moving!
Exhaust Stroke
The exhaust stroke cleans up. After the power party, gases must leave. The piston moves up again. It pushes the used gas out. The engine breathes out. It’s ready for more air and fuel.
The Role Of The Camshaft
The camshaft is an engine’s conductor. It makes sure valves open and close at the right time. Timing is key. Without it, the engine’s performance drops. The camshaft keeps everything in sync.
Harnessing Power: The Drivetrain
Imagine a powerful heart in a motorcycle.
It needs strong muscles to move the bike.
The drivetrain is like those muscles.
It uses engine power to spin the wheels.
The drivetrain plays a crucial role in your ride.
Transmission Mechanics
The transmission is a gearbox.
It has different gears for speed and power.
It works by:
- Gears change to match speed.
- Clutch engages, power flows to wheels.
- Shift lever helps you choose the gear.
Gear changes ensure smooth rides.
Final Drive Options
Final drive moves power from the gearbox to the wheel.
There are three types:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Chain Drive | Uses chain and sprockets |
| Belt Drive | Uses a rubber belt |
| Shaft Drive | Uses a shaft and gears |
Each type has its own benefits.
Chain drives are popular and easy to fix.
Belt drives are quiet and clean.
Shaft drives are strong and last long.
Choosing one depends on what you need.
Cooling And Lubrication: Preserving The Engine
Think of your motorcycle engine like an athlete, constantly running and generating heat. To perform well, it needs to stay cool and well-oiled. Cooling and lubrication play crucial roles in maintaining the engine’s health and longevity.
Air Vs. Liquid Cooling Systems
Motorcycle engines remain cool using air cooling or liquid cooling systems. Each system serves to prevent overheating but operates differently.
- Air cooling uses air flow to reduce heat. Fins on the engine increase surface area, which helps air take more heat away.
- Liquid cooling, or water cooling, involves coolant. This coolant absorbs engine heat and passes through a radiator where it cools down.
The Journey Of Engine Oil
Engine oil starts its journey in the sump, sitting below the engine. From there:
- A pump pushes it through a filter, catching any debris.
- It flows around the engine, reaching moving parts.
- Oiled parts reduce friction, protecting against wear and damage.
- Finally, oil returns to the sump, repeating the cycle.
This constant flow ensures the engine stays lubricated and cool.
Sound And Fury: Exhaust Systems
The roar of a motorcycle engine isn’t just about sounding impressive. It’s a complex symphony performed by the exhaust system, which is crucial for engine performance and noise management. Let’s uncover the secrets behind this vital component that gives bikes their distinctive growl and keeps them running efficiently.
Functionality Of Mufflers
Mufflers play a key role in diminishing the noise levels of a motorcycle. They work by redirecting exhaust gases and using a series of chambers and tubes to cancel out sound waves. Here’s how they function:
- Sound waves enter the muffler, moving through tuned chambers.
- These chambers are designed to reflect the waves and cause interference.
- This interference reduces the sound level as waves cancel each other out.
- The result is a quieter exhaust note exiting the motorcycle.
Emissions Control
Along with managing sound, exhaust systems are crucial in controlling emissions. They consist of several components dedicated to reducing environmental impact. Key parts include:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Oxygen Sensors | Monitor exhaust gases to optimize fuel combustion. |
| Catalytic Converters | Transform harmful gases into less dangerous substances. |
| Exhaust Valves | Regulate the flow of gases to maintain engine pressure. |
These parts work collectively to ensure the bike meets legal standards for air quality. They efficiently process and expel exhaust gases, making sure the motorcycle rides clean and green.

Credit: www.bennetts.co.uk
The Evolution Of Motorcycle Engines
From roaring to purring, motorcycle engines have transformed over the years. This journey is not just about power but also innovation and engineering. Let’s dive into how these engines have evolved through time and what the future holds.
Historical Milestones
The saga of motorcycle engines is rich with milestones. Each era brought unique designs and technological leaps.
- 1885: Gotlieb Daimler crafts the first motorcycle with an engine— a wooden frame housing a single-cylinder four-stroke engine.
- Early 1900s: Multi-cylinder engines emerge, paving the path for today’s motors.
- Post-WWII: Technology surges, motorcycles become a symbol of freedom with better engines.
- 1990s: Digital ignition and fuel injection systems improve efficiency and performance.
Future Technologies In Engine Design
The engines of tomorrow promise leaps in performance and eco-friendliness. Innovation is buzzing in the motorcycle engine realm.
| Technology | Impact |
|---|---|
| Electric Motors | Zero emissions, instant torque, and reduced maintenance. |
| Variable Valve Timing | Enhanced power and efficiency across RPM ranges. |
| 3D Printed Components | Lighter and stronger parts that push boundaries of engine design. |
| Hydrogen Fuel Cells | A potential future where only water is the exhaust. |
With every piston movement and spark, engineers are writing the next chapter of motorcycle engines. Exciting times lie ahead for riders and tech enthusiasts alike.
FAQ
How Does A Motorcycle Work Step By Step?
A motorcycle operates through a sequential process: the engine combusts fuel to generate power, which then transfers via the transmission to the chain or belt. This action rotates the rear wheel, propelling the motorcycle forward. Meanwhile, the rider controls direction using the handlebars and manages speed with throttle and brakes.
How Does A Motorcycle Ignition System Work?
A motorcycle ignition system sparks the engine by generating a high voltage pulse. The battery sends current to the ignition coil, which amplifies the voltage. This high voltage arcs across the spark plug’s gap, igniting the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber to start the engine.
How Does A Bike Engine Start?
A bike engine starts when the ignition switch activates, sparking a fuel-air mixture combustion via the spark plug. This ignition process sets the pistons in motion, turning the crankshaft and initiating engine operation.
How Many Pistons Does A Motorcycle Engine Have?
Motorcycle engines can have between one and six pistons, depending on the model and design. Common configurations include single, twin, triple, four, and six-cylinder options.
Bottom Line
It is essential to know how a motorcycle engine works for every rider. We’ve uncovered the basics of their operation, from combustion to transmission. This knowledge enhances not only the joy of riding but also maintenance skills. Ride confidently, with a newfound appreciation for the heart of your two-wheeled machine.



Leave a Reply